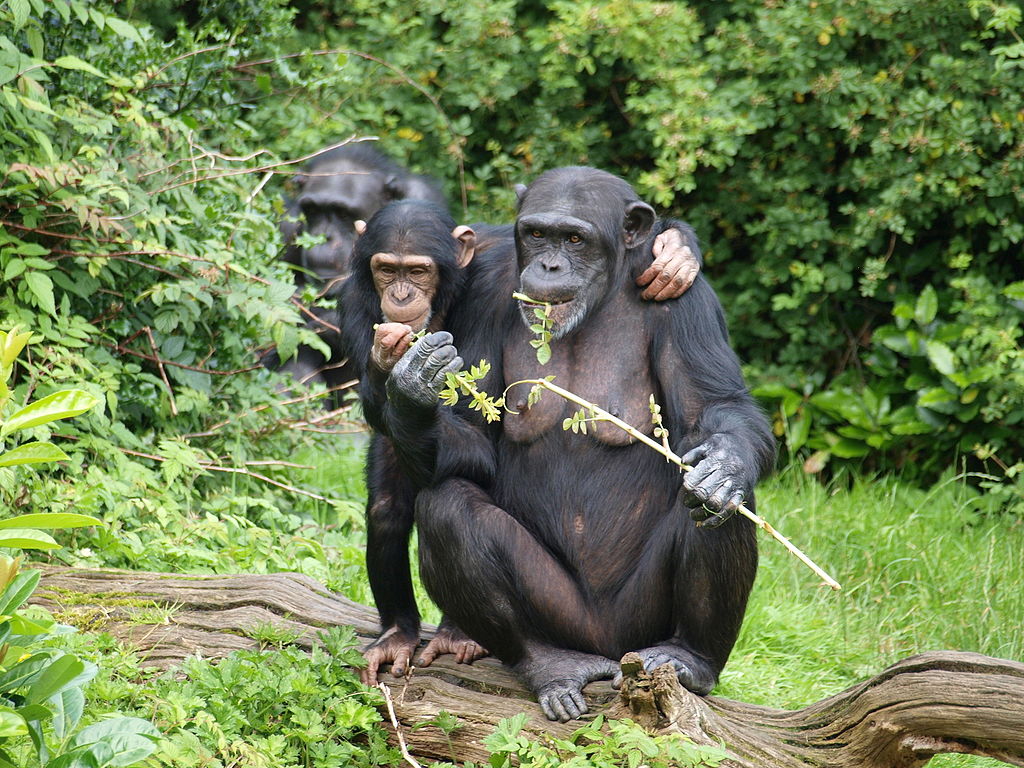
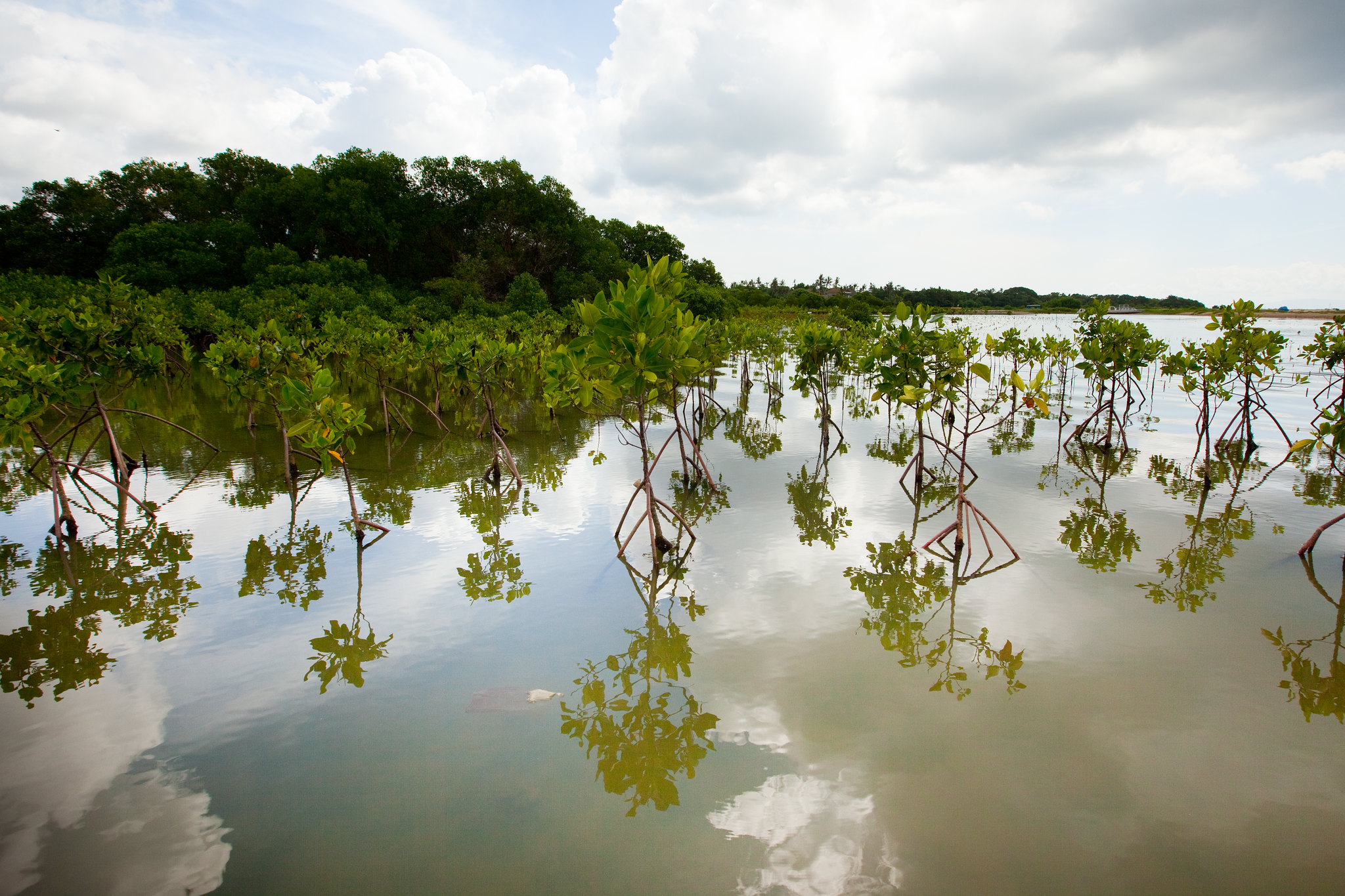
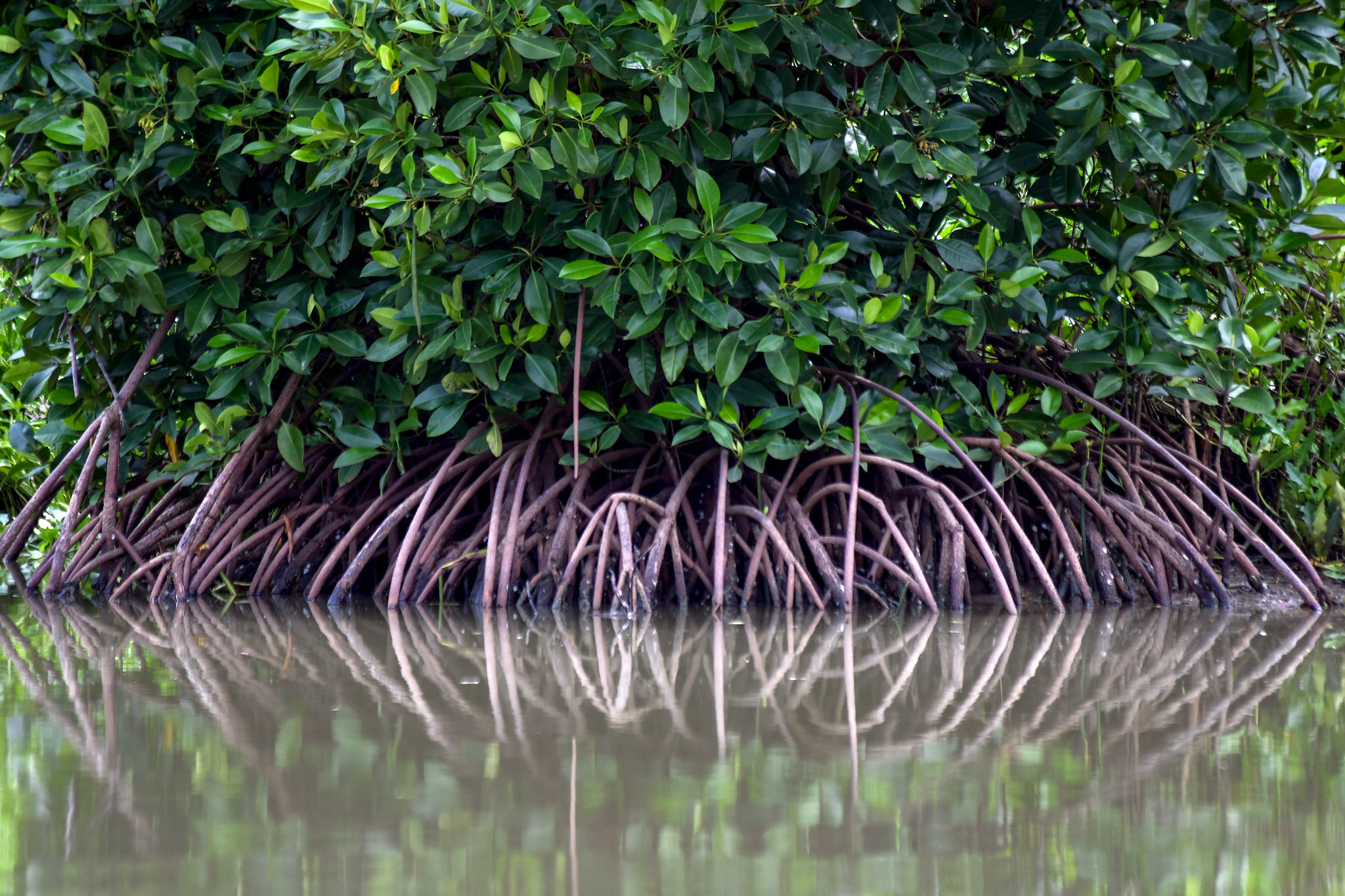
Douala – Edea coastal Atlantic area is a confluence estuarine basin of four of Cameroon largest rivers: Rivers Wouri, Dibamba, Sanaga and Nyong covering over 500 000 ha presenting a unique coastal and marine wetlands type of the Cameroon Estuary including the mangroves, lakes, lagoons, tropical lowland Congolian rainforest with marshes and swamps. Over 200 terrestrial and water bird species and 120 fish species, large mammalian flagship species including forest elephants, primates (chimpanzees, monkey species especially black Colobus), antelopes (sitatunga, blue duiker, etc) abound in adjoining rainforest.
Although considerable efforts have been made to conserve the rich wildlife and biological diversity of the Douala-Edea, the area is still faced with serious poaching and illegal exploitation of natural resources for commercial rather than domestic purposes. For example, elephant population of the reserve has significantly dropped over the years as a result of poaching and ivory trade with probably less than 50 individuals still found in the area. Other endangered and high conservation valued species include West African manatees and sea turtles which are also heavily hunted.
Detailed inventories have been carried out to assess fish biodiversity of the area. There is data and information available through surveys and other research studies on sea turtles, elephants, chimps, West African manatees especially their seasonal movement patterns from radio-collared individuals etc.
Priority Actions
The following are main activities that will be carried out for protection and management of flagship species populations.
- Update biological data on population status of West African manatees including threat levels and produce maps on movement and distribution patterns
- Information gathering on population status of chimps, elephants and other important wildlife species
- Assessment of existing threats and critical breeding sites of sea turtles within the Atlantic coast of Douala-Edea wildlife reserve